Dog / Detail
Chewing the Hard Stuff: Why Your Dog Loves Doors, Windows, and Hangers?
Jonathan Bennet | 18 September 2024 | 18:05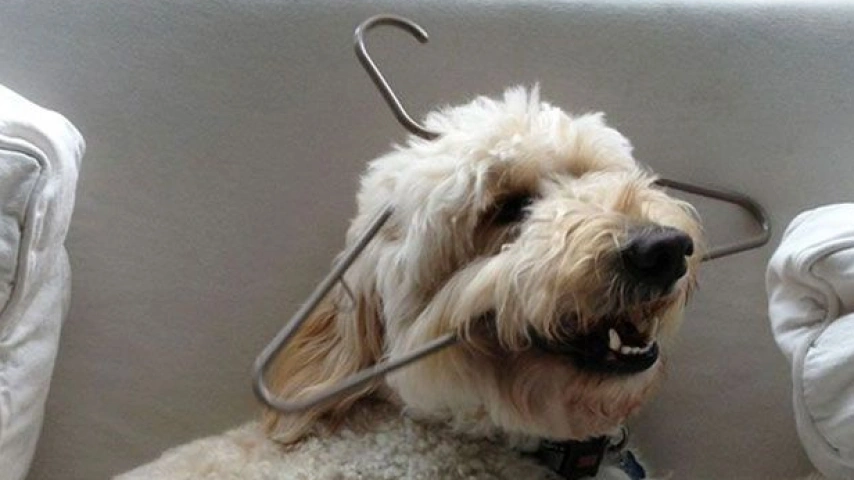
Chewing is a natural and essential behavior for dogs. It serves various purposes, from dental hygiene to stress relief.
While most dogs prefer softer toys, some develop a taste for harder objects like doors, windows, and even plastic hangers. This might seem destructive, but there are underlying reasons for this behavior.

Why Do Dogs Chew Hard Objects?
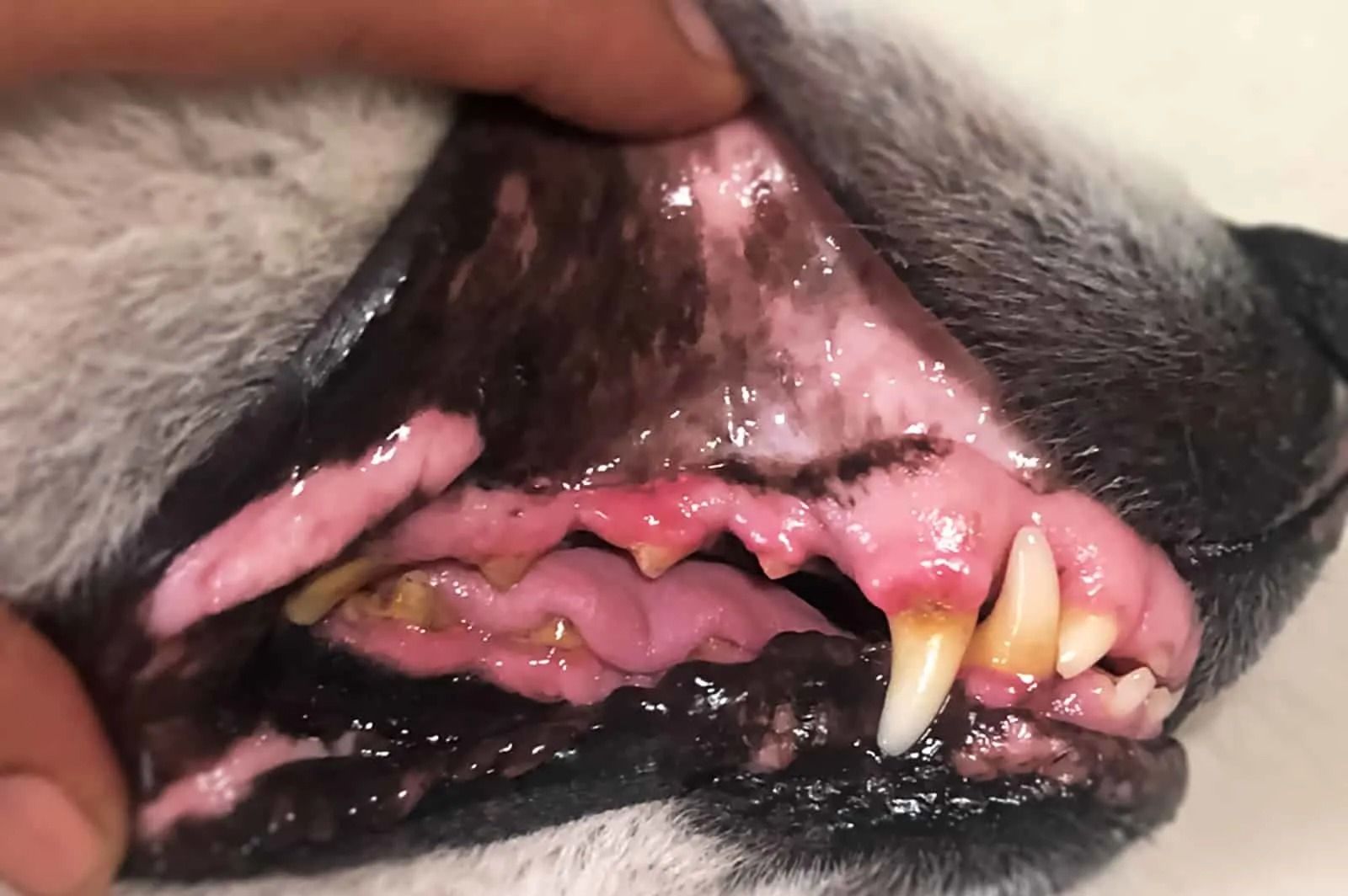
- Dental Health: Just like humans, dogs need to keep their teeth clean. Chewing on hard objects can help remove plaque and tartar buildup, promoting healthier gums.
- Boredom and Frustration: Dogs, like humans, can get bored. When they lack sufficient mental or physical stimulation, they may resort to destructive chewing as a way to relieve boredom or frustration.
- Separation Anxiety: Some dogs may exhibit excessive chewing as a symptom of separation anxiety. When left alone for extended periods, they may chew to cope with stress and anxiety.
- Teething: Puppies, in particular, may chew on hard objects to soothe their sore gums during the teething process.
- Instinct: Dogs' ancestors, wolves, were hunters who chewed on bones and other hard materials to strengthen their jaws and teeth. This instinctual behavior may still be present in domesticated dogs.
Is It Normal?
While chewing is a normal canine behavior, chewing on hard objects that can cause damage to your home is not ideal. It's important to redirect your dog's chewing behavior toward appropriate toys and chew bones.
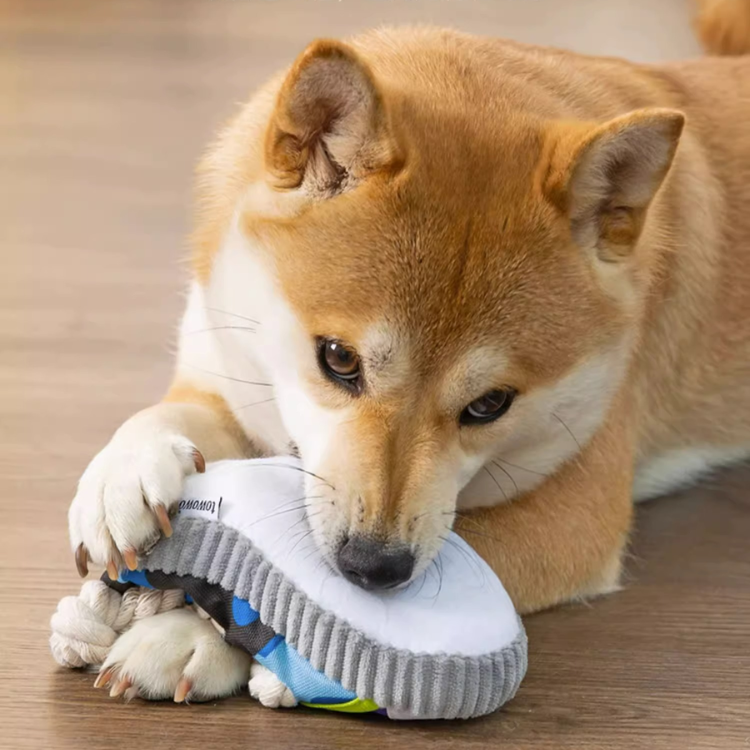

How to Redirect Your Dog's Chewing
- Provide Appropriate Chew Toys: Offer your dog a variety of chew toys, including Kongs, Nylabones, and durable rubber toys. Fill Kongs with treats or peanut butter to make them more enticing.
- Mental Stimulation: Engage your dog in mentally stimulating activities like training sessions, puzzle toys, and interactive games.
- Exercise: Ensure your dog gets enough daily exercise to keep them physically and mentally stimulated.
- Address Underlying Issues: If you suspect your dog's chewing is due to separation anxiety or another emotional issue, consult with a veterinarian or animal behaviorist.
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward your dog for chewing on appropriate toys and discourage chewing on inappropriate objects.

Preventative Measures
- Make your home less attractive: Remove or secure items that your dog might find tempting to chew.
- Bitter apple spray: Apply bitter apple spray to objects you want to protect.
- Supervised chewing: Monitor your dog while they are chewing to ensure they are using appropriate toys.

When to Seek Professional Help
If your dog's chewing behavior is severe or causing significant damage, it's advisable to consult with a veterinarian or animal behaviorist. They can help you identify the underlying causes and develop a tailored behavior modification plan.
Remember: While chewing on hard objects may seem destructive, it's often a natural behavior that can be redirected with patience and positive reinforcement. By providing appropriate chew toys, mental stimulation, and addressing any underlying issues, you can help your dog develop healthy chewing habits.
Related
-

The Healing Power of Dogs: How Canine Therapy is Revolutionizing Mental Health and Boosting Positive Energy in Humans
Dog14 November 2024
-

A Pawsitive History: Dogs of Nuremberg
Dog09 November 2024
-

The Role of Oxytocin in the Human-Dog Bond: The Science Behind Our Deep Connection
Dog06 November 2024
-

Beyond the Beach: Jamaica's Dog Lovers
Dog29 October 2024
-

A Dog's Delights: Homemade Snacks for Our Furry Babies, Recipes Included!
Dog29 October 2024
-

A Dog's Disorientation: Understanding Your Dogs' Wanderlust
Dog29 October 2024
Popular
-

-

A Pawsitive History: Dogs of Nuremberg
09 November 2024 -

-

Beyond the Beach: Jamaica's Dog Lovers
29 October 2024 -
